Chapter 6 Continuous Probability Distributions
Ad Enjoy low prices on earths biggest selection of books electronics home apparel more. Chapter 6 Continuous Probability Distributions Uniform Probability Distribution Normal Probability Distribution Exponential Probability Distribution.
Continuous Probability Distributions Basic Introduction Youtube
View Chapter 6_ Continuous Probability Distributionspdf from IS 310 at California State University Long Beach.

. Height blood pressure and cholesterol level. A continuous probability distribution. Read customer reviews find best sellers.
QRM Chapter 6 - Continuous Probability Distributions. Its probability density function is bell shaped and determined by its mean u and standard deviation o. Ad Parents nationwide trust IXL to help their kids reach their academic potential.
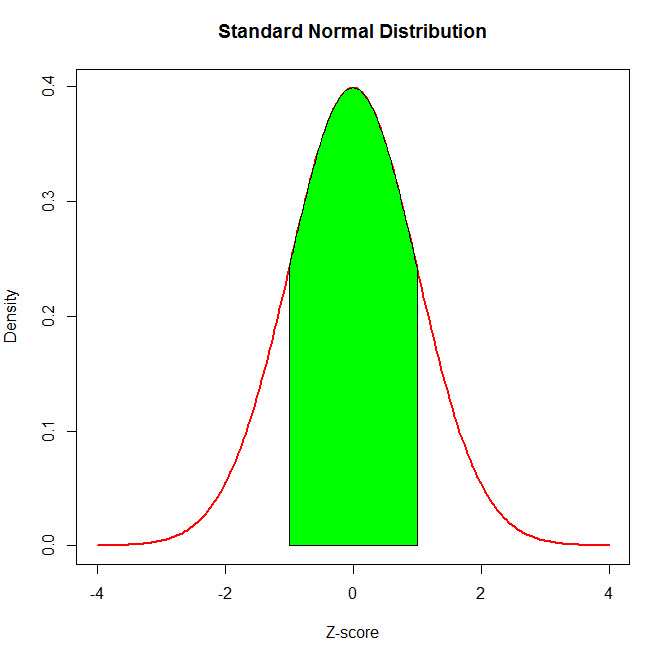
Browse discover thousands of brands. Some Continuous Probability Distributions 64 ApplicationsoftheNormalDis-tribution z-score z x m s is often called the z-score. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.
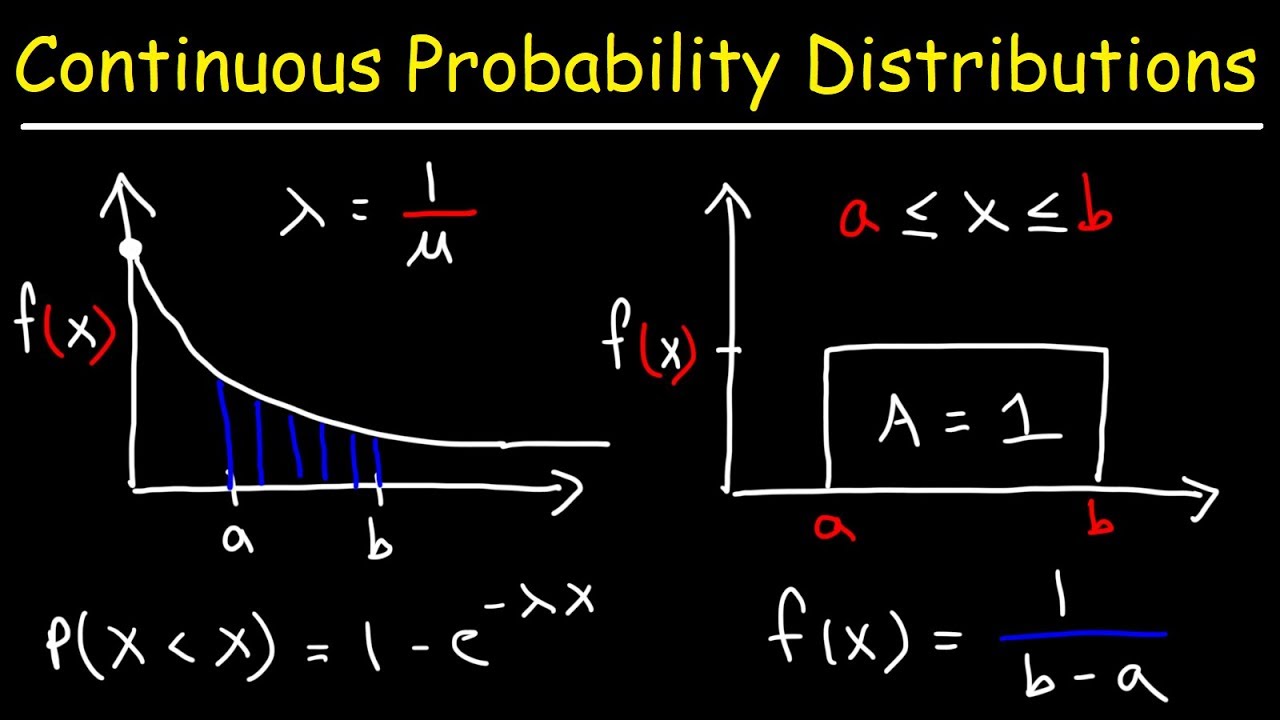
6-4 Uniform Distribution Probability. Slides by John Loucks St. Up to 3 cash back Chapter 6 Continuous Distributions - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation ppt PDF File pdf Text File txt or view presentation slides online.
2003 John Wiley Sons. It measures the number of standard deviations that a data value x is from the mean m. Business Statistics 4e by Ken Black.
Quantitative Research Methods 5th Ed by Johnathan Mun PhD. Know how to compute probability values for a continuouable to compute the expected value and variance for such as uniform probability distribution and be distribution. Understand the difference between how probabilities are computed for discrete and continuous random variables.
Enter your email for an. Get 247 study help with the Numerade app for iOS and Android. A continuous uniform random variable x has a lower bound of a -21 an upper bound of b -6.
Continuous Probability Distributions 178 Section 62. Compute the area under the standard normal curve to the right of z 83. Continuous Probability Distributions Continuous Probability Distributions A continuous random variable can assume any value in an interval on the real line or in a collection of intervals It is not possible to talk about the probability of the random variable assuming a particular value Instead we talk about the probability of the random variable assuming a value.
Unlimited math practice with meaningful up-to-date tracking on your childs progress. A continuous probability distribution that is useful in computing probabilities for the time it takes to complete a task. It is not possible to talk about the probability of the random variable assuming a particular value.
Scribd is the worlds largest social reading and publishing site. F x. A normal distribution with a mean of zero and a standard deviation of one.
CHAPTER 6 CONTINUOUS PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS Last modified by. Uniform Probability Distribution Normal Probability Distribution Exponential Probability Distribution. A continuous probability distribution for which the probability that the random variable will assume a value in any interval is the same for each interval of.
Continuous Probability Distributions Continuous Probability. When x is smaller than the mean m z is negative. However not every bell shaped curve is a normal curve.
2 Continuous Probability Distributions 1 of 2 A continuous random variable can assume any value in an interval on the real line or in a collection of. A continuous random variable can assume any value in an interval on the real line or in a collection of intervals. Up to 15 cash back Chapter 6.
Chapter 6 Continuous Probability Distributions. Edwards University Cumulative Probability Table for the Standard Normal Distribution Pz 83 Standard Normal Probability Distribution Pz 83 1 Pz 83 1- 7967 2033 Solving for the Stockout Probability Step 3. Or posted to a publicly accessible website in whole or in part.
What is p x -1. It is not possible to talk about the probability of the random variable assuming a particular value. Video answers for all textbook questions of chapter 6 Continuous Probability Distributions Statistics for Business Economics by Numerade.
Chapter 6 Continuous Probability Distributions Uniform Probability Distribution Normal Probability Distribution. P x X x x x 2 1 1 ba 2 45 42 1 47 41 2 f x 45 42 1 P 42 X 45 47 41 2. Chapter 6 Continuous Probability Distributions Learning Objectives.
When x is larger than the mean m z is positive. What value of x provides an area in the upper tail equal to 020. Chapter 6 Continuous Probability Distributions.
Slideshow 851837 by myra. Start studying Chapter 6. Graphs of the Normal Distribution Many real life problems produce a histogram that is a symmetric unimodal and bell-shaped continuous probability distribution.
Chapter 6 Continuous Probability Distributions Uniform Probability Distribution Normal Probability Distribution Standard Normal Probability. A continuous uniform random variable x has a lower bound of a -3 an upper bound of b 5. Instead we talk about the probability of the random variable assuming a value within a given interval.
Quickly memorize the terms phrases and much more. A continuous random variable can assume any value in an interval on the real line or in a collection of intervals. Up to 3 cash back Chapter 6 Continuous Probability Distribution - View presentation slides online.
Continuous Probability Distributions Env710 Statistics Review Website
Continuous Probability Distributions Env710 Statistics Review Website
Continuous Probability Distributions Env710 Statistics Review Website

Continuous Probability Distribution An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
No comments for "Chapter 6 Continuous Probability Distributions"
Post a Comment